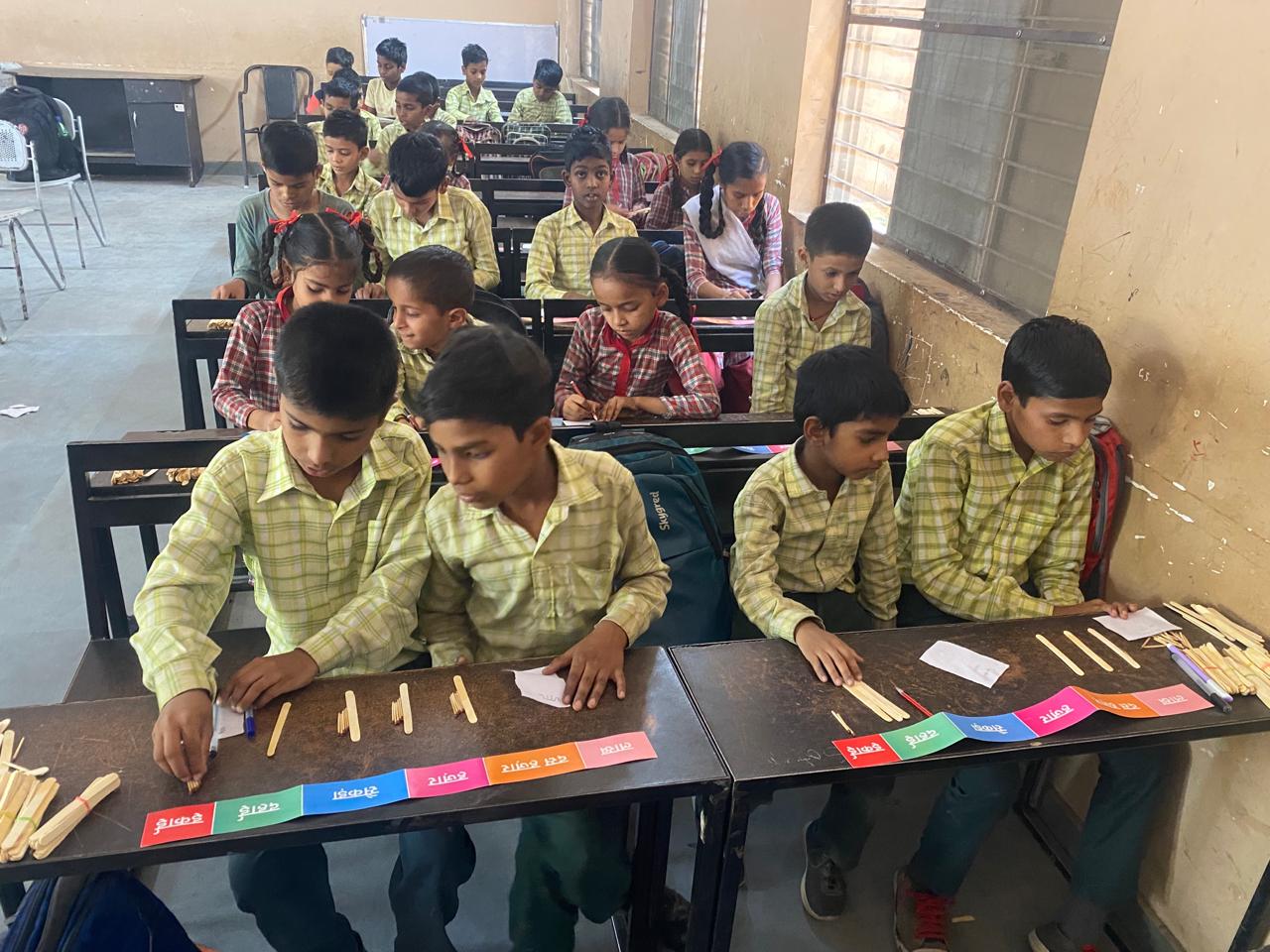
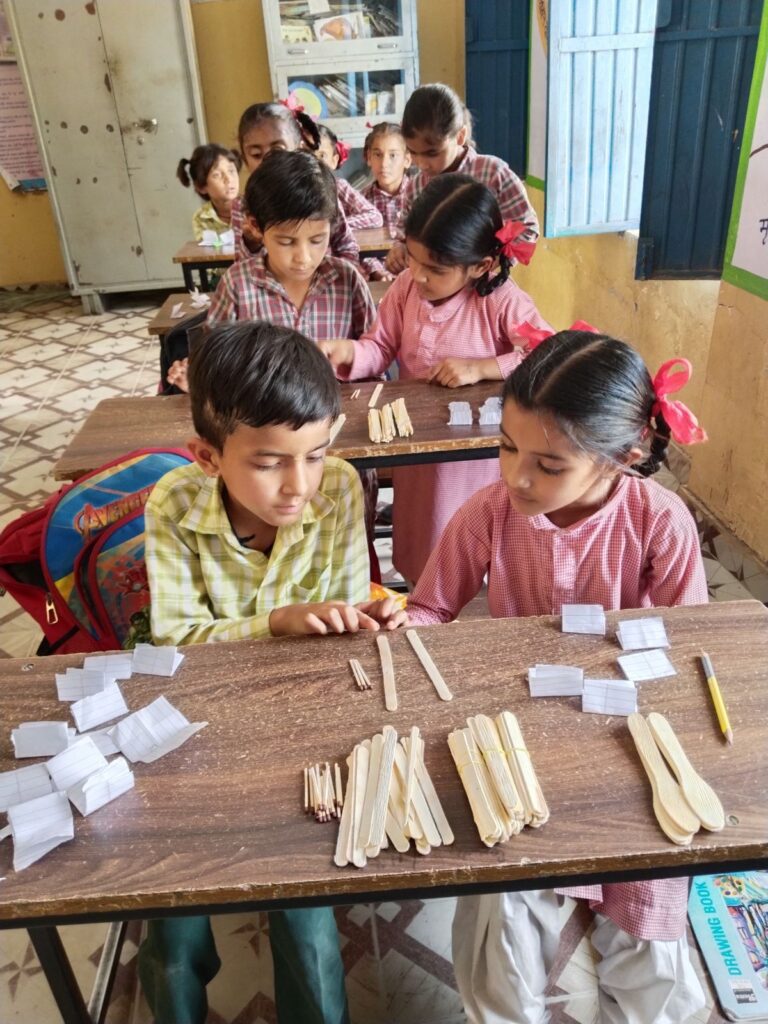
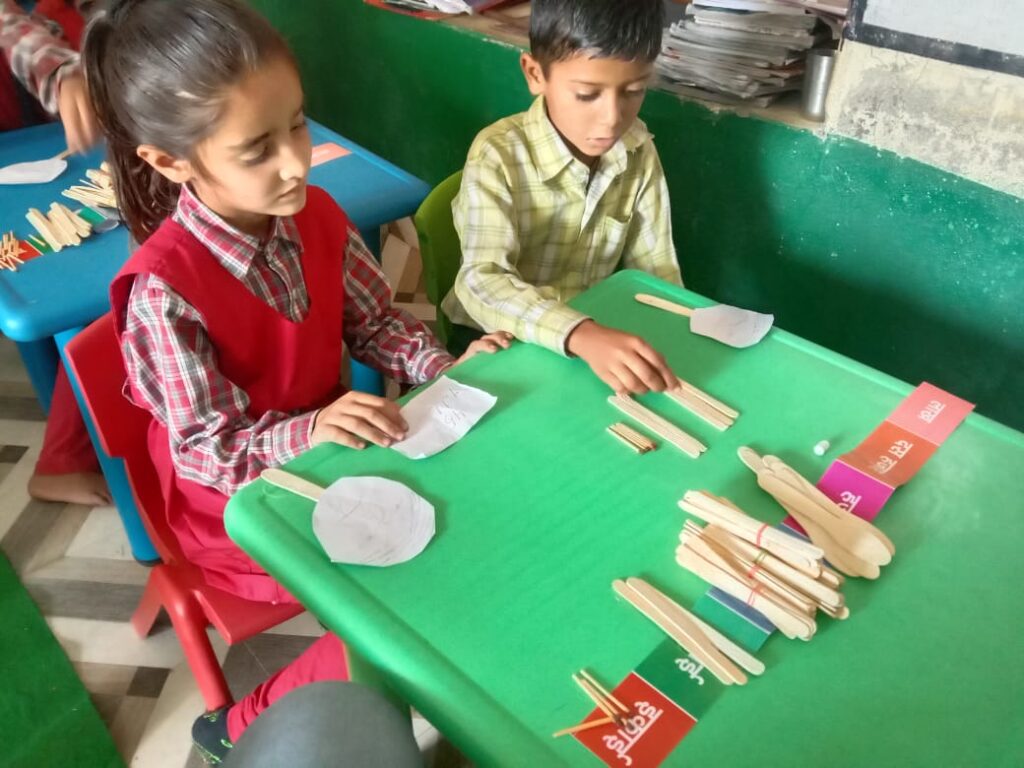
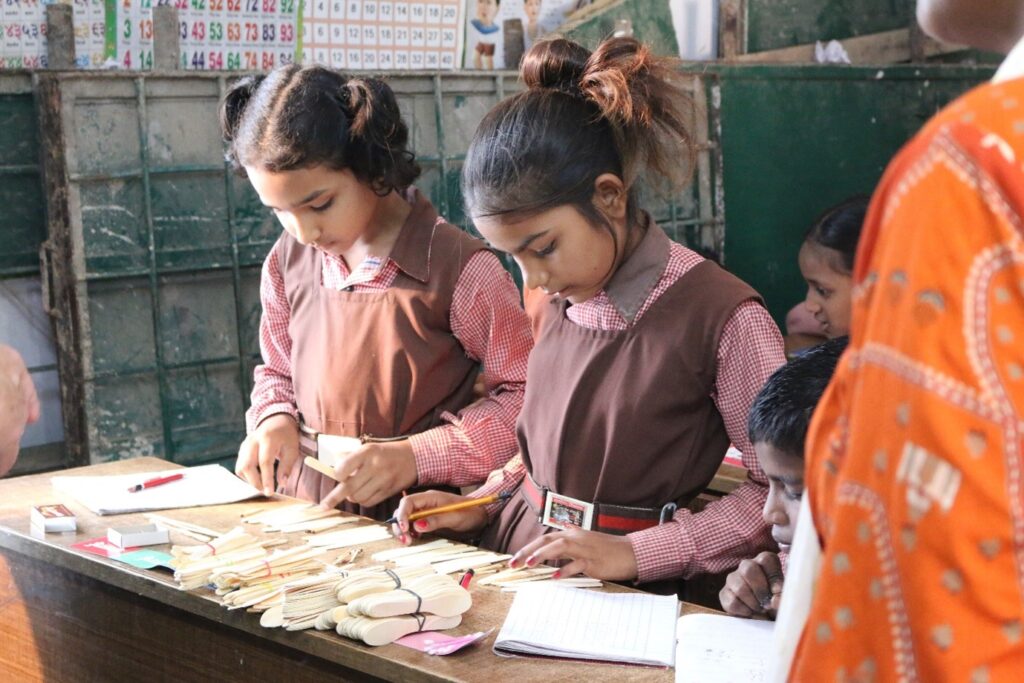
The Peepul Math toolkit empowers teachers in resource-constrained classrooms by making math engaging and experiential
Peepul partners with government systems (currently with Govt. of Madhya Pradesh and Municipal Corporation of Delhi) to create high-engagement classrooms, ensuring children from low-income backgrounds learn and thrive. Through teacher development, academic mentorship, and governance strengthening, the organization transforms public school education—empowering every child to reach their full potential with confidence and pursue a fulfilling future.
Peepul believes that foundational numeracy is the bedrock of mathematical learning—without it, children struggle as concepts grow more complex. NAS survey data shows a steady decline in math performance across grades, highlighting the urgent need for strong early foundations. The not-for-profit organization vision is to equip every teacher with practical, engaging tools that make math accessible, meaningful, and lasting.

Math is everywhere—woven into the fabric of our daily lives. Yet, for young learners, it remains an abstract and intimidating subject. Teachers, especially in resource-constrained classrooms, struggle to bridge this gap, often lacking the time and materials needed to make math truly engaging. The Peepul Math toolkit was developed to address this gap and accelerate foundational numeracy outcomes after the pandemic, making it a game-changer for foundational numeracy. This toolkit isn’t just about resources—it’s about bringing pedagogy to life, ensuring that children don’t just memorize math, but truly understand and experience it.
What Is the Math Toolkit?
The Peepul Math Toolkit is a carefully designed collection of teaching-learning materials (TLMs) and manipulatives that make math engaging and accessible for foundational grades. Aligned with NIPUN Bharat, the National Curriculum Framework (NCF), NCERT textbooks, and insights from the Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education, it translates complex concepts into hands-on, interactive learning experiences. Reviewed by math experts and curriculum developers and piloted by teachers, the toolkit seamlessly integrates into daily classroom instruction.
With 13 types of manipulatives and activity cards, the Math Toolkit focuses on Number Sense and Number Operations, offering ready-to-use, research-backed resources for group and individual learning. Additionally, the Math Meeting template book helps teachers set up an interactive Math Wall, making daily revision engaging and effective.

The toolkit is designed to maximize student practice, offering both shared and individual learning opportunities. In the foundational years, children need hands-on experience with manipulatives—both concrete and pictorial—to build a strong conceptual base before transitioning to abstract mathematical ideas. By going beyond textbooks, the toolkit empowers teachers to create dynamic, interactive math lessons, where students actively explore, reason, and articulate their thinking.
The use of the math toolkit encourages deeper cognitive engagement, ensuring that learning is student-driven rather than teacher-dependent.
Beyond convenience, the toolkit also promotes cost-effective and sustainable teaching. Many of the activities can be easily replicated using everyday materials like newspapers and wastepaper, making it a practical, scalable solution for diverse classrooms.
The toolkit also comes with a teacher manual that gives descriptions and instructions on how to use the different cards, how it can be adapted for different levels of learning.

From Training to Classrooms – The toolkit implementation
While the Peepul Math Toolkit is a stand-alone resource that any teacher can use for foundational numeracy lessons, its impact is maximized when integrated into structured teacher training. It is introduced during numeracy capacity-building modules for Grades 1–3 teachers as a supplement to NCERT textbooks and teacher lesson plans. The assumption is that teachers can make the most of the toolkit when they have a strong foundation in numeracy pedagogy, including the Concrete-Pictorial-Abstract (CPA) approach, math-talk, and math-meetings.
Implementation follows a holistic pathway—starting with capacity building on content, pedagogy, and TLMs, followed by ongoing coaching and feedback as teachers incorporate these strategies into their classrooms. By embedding the toolkit within this structured support system, Peepul ensures that it is not just an additional resource but a catalyst for meaningful and sustained improvements in math teaching and learning.
Measuring Change
In 2023, Peepul, in collaboration with Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD), piloted the Math Toolkit in one zone—Karol Bagh—to test its effectiveness in improving foundational numeracy instruction. Following teacher training, classroom observations in 57 schools revealed promising early adoption: 60% of teachers used the Math Meeting template daily for revision, 77% integrated learning outcome-aligned TLMs, and 60% actively used the Peepul Math Toolkit in their lessons.
Encouraged by these results, MCD requested a scale-up to all 12 zones spanning 1,573 schools, ~19,000 teachers and 6.4 lakh students. To ensure system-wide adoption, Peepul worked closely with Mentor Teachers and the MCD Curriculum Team to co-create a customized version of the toolkit. This refined version was mapped to MCD’s foundational numeracy module levels, making it seamlessly align with teachers’ existing lesson plans.
In 2024, the toolkit was distributed across all MCD schools, with Mentor Teachers leading the training through school-based and online workshops. To assess its real-world impact, Peepul and Mentor Teachers conducted joint classroom observations of 147 teachers. The findings were promising—29% (42 teachers) effectively used the toolkit to teach concepts, a significant milestone given that this adoption was entirely system-led.
In 2024, Peepul also initiated a toolkit-impact study in the pilot zone to test for impact of the toolkit usage on student engagement and numeracy outcomes. The incoming early data indicates that the toolkit is being continually used in 54% of the classrooms (sample size-98 classrooms). Additionally, in 48% of these math lesson observed, student engagement was more than 50% due to the use of the toolkit cards by the teachers (student engagement defined as percentage of students on task). The impact result on numeracy SLOs is still awaited but the organization is hopeful that with correct and consistent use of the toolkit the foundational numeracy outcomes will improve in these classrooms.
This journey from a pilot in one zone to full-scale implementation highlights the power of government-led reform, strategic co-creation, and teacher-driven change. For educators, nonprofits, and policymakers passionate about strong foundational learning, the Peepul FLN Math Toolkit is more than a resource—it’s a step toward reimagining math classrooms across India.
Trials, Triumphs, and Takeaways
A key challenge with scaling any teaching-learning material is the associated cost implication of producing and disseminating it systemwide. While Peepul has funded the math toolkit scale-up this year, there is hope for a sustainable approach that will allow government systems to adopt it effectively.
Adoption has also been smoother in pilot zones where teachers received structured training and support, but at scale, the absence of a formal mandate and ongoing capacity building might slow down adoption rate and effectiveness.
Many of these challenges can be addressed by strengthening system collaboration, advocating for institutionalization, and building system capacity. Cost-effective replication can be enabled by hosting toolkit PDFs on system portals, embedding toolkit activities into standardized lesson plans, and training the system’s academic coaches to enhance classroom implementation.
Allies in Action
The Peepul Math Toolkit’s success stems from strong partnerships with MCD, driving system-led adoption. MCD customized the toolkit to align with FLN module levels, while Mentor Teachers championed its implementation through training, workshops, and classroom observations. Strengthening these partnerships will ensure long-term sustainability and lasting impact on foundational numeracy in public schools.
Scaling the Peepul Math Toolkit for Systemic Impact
The Math Toolkit is already driving change in MCD schools, with teachers integrating it into daily instruction. Encouraged by its impact, system stakeholders have requested a similar intervention for foundational literacy. In response, Peepul is strengthening and customizing the Hindi Literacy Toolkit for scale. Originally developed and piloted in erstwhile SDMC between 2018-2020, this toolkit is now more relevant than ever, given the current gaps in Hindi foundational literacy achievement.
Additionally, English remains an aspirational language for both the system and stakeholders, yet access to effective pedagogy and teaching resources in early grades remains limited. Looking ahead, the non-for-profit organization plans to develop and pilot an English Phonics Toolkit, along with capacity-building modules for teachers. Based on early adoption and system readiness, Peepul aims to scale this intervention to further strengthen foundational literacy in MCD schools.

“Looking ahead, we see a future where every child experiences the joy of math through engaging, hands-on learning. Our vision is for these toolkits to become an integral part of every math lesson, not just in select classrooms but across entire school systems. For lasting impact, this initiative must evolve from a Peepul-driven effort into a government-owned and government-funded model,” shares Urmila Chowdhury, Co-founder, Peepul.

“By deepening our partnerships with education departments at the city and state levels, we aim to empower governments as the driving force behind this transformation—ensuring that every teacher has access to these tools, every classroom benefits, and every child builds a strong foundation in math. The journey ahead is exciting, and with collective commitment, we can reimagine math learning at scale,” feels Sonia Mondal, Deputy Director, Peepul.